- Details
- Hits: 26135
 In the old Roman Agora on the slope of Athen's ancient Acropolis hill is the Tower ofWinds. Today, completing two years of restoration, the interior was re-opened to the public this summer in August, 2016. The Tower had been closed for the last 200 years. The story of the Tower starts in the first century, BCE, probably during the reign of Julius Caesar.
In the old Roman Agora on the slope of Athen's ancient Acropolis hill is the Tower ofWinds. Today, completing two years of restoration, the interior was re-opened to the public this summer in August, 2016. The Tower had been closed for the last 200 years. The story of the Tower starts in the first century, BCE, probably during the reign of Julius Caesar.
The Tower was designed by Andronikos Kyrrhestos (Andronicus of Cyrrhus), an astronomer and maker of celestial instruments. Andronicus constructed a white marble sundial for the sanctuary of Poseidon and Amphitrite on the island of Tinos. The sundial becamse so famous that Andronicus was invited to Athens where he erected the magnificent 14 meter Tower called the Aerides (the Winds) . It was built on the eastern side of the Roman Agora in Athens and meant to have utilitarian value. "No one knows who funded its lavish construction - the octagonal monument is made almost entirely of Pentelic marble, the same used for the Parthenon and rarely found in buildings other than temples," said Stelios Daskalakis, head conservator.
Atop of the octogon tower now rests the fully-preserved roof made of 24 marble slabs, resting on a Corinthian capital. Once a bronze statue of Trition, the god of the sea, was set on the roof to turn in the wind as a weather indicator. By night, water flowed through a hydro-mechanical system designed by Andronicus from a cylinder inside the Tower. The water level lead to an exterior indicator creating a night time clock or clepsydra. During the day the Tower was a public time teller with eight sundials.
- Details
- Hits: 28382
|
|
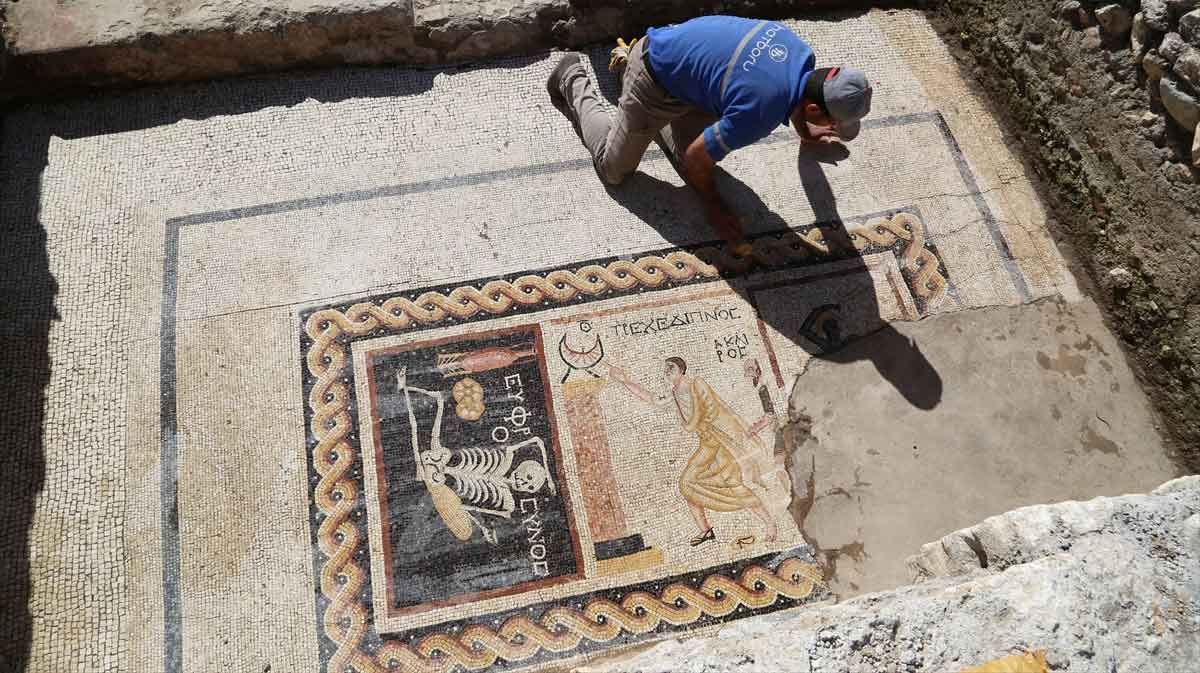
The Daily Sabah reports a 2,400 year old mosaic discovered during excavations in Turkey's southern Hatay provice that shows a skeleton that according to archeologist Demet Kara fromthe Hatay Archeology Museum has an inscription that translates from ancient Greek to say "Be cherrful, and live your life."
Perhaps more interesting to sundialists is the mosaic further right. It is of a Roman attending the bath. Demet Kara explains, "...there is a sundial and a young clothed man run[s] towards it with a bare-headed butler behind. The sundial is between 9 and 10 am. 9am is the bath time in the Roman period. He has to arrive at supper at 10am. Unless he can, it is not well received. There is writing on the scene that reads he is late for supper and writing about time on the other."
Kara added, "[This is] a unique mosaic in Turkey. There is a similar mosaic in Italy but this one is much more comprehensive. It is important for the fact that it dates back to the third century BCE...Antiocheia was a very important, rich city. There were mosaic schools and mints in the city. The ancient city of Zeugma in [the southeastern province of] Gaziantep might have been established by people who were trained here. Antiocheia mosaics are world famous."
- Details
- Hits: 18650

Kānaloa Stone Shadow Alignment
Photo: Kaho'olawe Island Reserve Commission
|
On Kaho'olawe, the smallest island of the Hawaiian island chain only 7 miles from Maui, sits an endangered and sacred rock, the Kānaloa, with petroglyphs and a row of 32 cupules (man-made depressions) along one edge. “It has significant celestial alignments with the rising and setting of the sun,” said Michael Naho'opi'i, Executive Director of the Kaho'olawe Island Reserve Commission (KIRC). It appears that there is a relationship between the shadow of a stick held vertically along lines etched in the stone and the cupules.
Documented as Site 110 feature BU, the Kānaloa stone is relatively flat and rests on a natural pedestal that when tapped, resonates with a bell-like ring. But its petroglyphs and alignment cups may soon topple into a nearby and ever growing ravine. In 2010 the Commission approved "The Cultural Use Plan: Kūkulu Ke Ea A Kānaloa" with one of the recommendations to preserve and stabilize the stone. The first phase of the plan has been to document the stone's celestial alignments and quantify the erosion forces acting on its base.
- Details
- Hits: 19793
Larisa N. Vodolazhskaya of the Department of Space Physics at Southern Federal University (SFU), Rostov, has brought two ancient time keepers together with a new and startling result. The story starts at the turn of the end of the 19th century with the discovery of an L-shaped bar found in the tomb of Thutmose III (1479-1425 BCE). that appeared to be a sundial. In the 1930's a "user manual" of sort was found carved on the tomb ceiling of Seti I (1290-1279 BCE) at Abydos. The ideal L-shaped bar had lines engraved with distances from a starting mark of 3, 6, 9, and 12 units. The Seti I text describes these spacings as "an established procedure". But what is the procedure?
- Details
- Hits: 15288
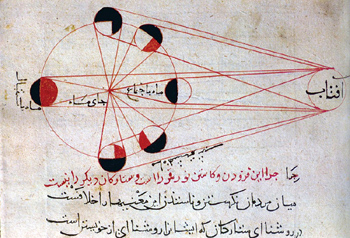
Al-Biruni's diagram of the moon's phases.
Credit: photo reproduction from Seyyed Hossein Nasr, Islamic Social Science: An Illustrated Study (World of Islam Festival Publishing Co., 1976).
Photo use for non-profit educational purposes only.
|
Ibn al-Shatir, whom we give credit for inventing the first modern sundial with gnomon pointing to the celestial pole in 1371 C.E., is but one of many scientific scholars of Central Asia during the “Eastern Renaissance” that lasted from about 800 to 1500 C.E. In this week’s issue of Science, [20 June 2014] Richard Stone reviews the accomplishments of Abu Rayhan al-Biruni (born 973 C.E.) and the possibility that he "discovered" the American continent.
Situated at the crossroads of cultures from China, India, the Middle East, and Europe, al-Biruni was an acomplished astronomer at an early age. At 16 he measured the height of the midday sun and calculated the latitude of his hometown, now in present day Khiva, Uzbekistan.
- Details
- Hits: 26246
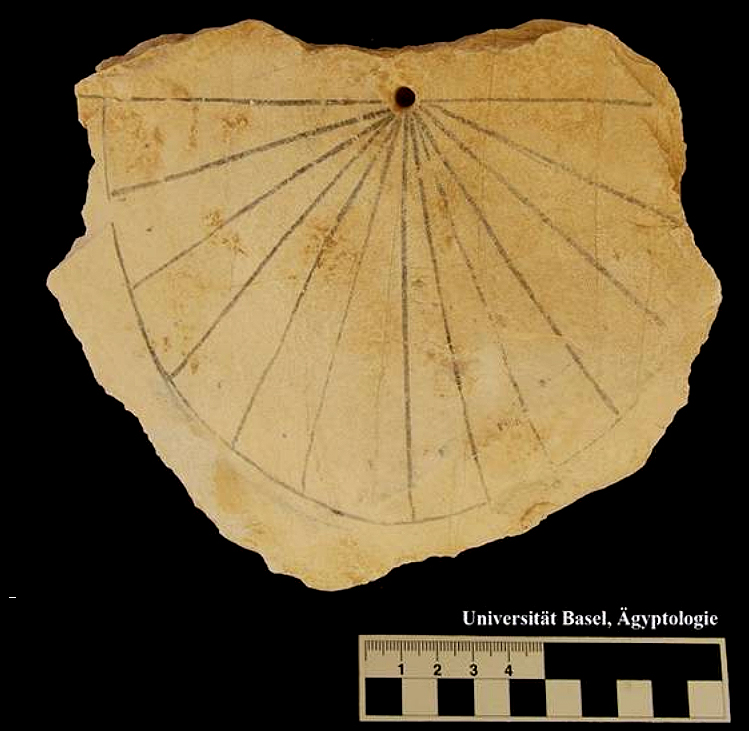

[photo Courtesy University of Basel]
|
Professor Dr. Susanne Bickel and her archeological team from the University of Basel found one of the oldest sundials in the world during this year’s excavation in the Valley of the Kings. A limestone sundial was found near tomb KV61 during a survey of the surface rubble. The location of the dial corresponds to an area where there are remains of workmen’s huts dating to the Ramesside Period of the 13th century BCE.
The dial was most likely a vertical, south facing sundial. The horizon line of the dial is about 16 cm across with a hole at the mid point to hold a simple horizontal metal rod or wood stick gnomon, indicating that the gnomon displayed shadows of temporal (seasonally uneven) hours. The limestone dial has a black painted semicircle. On each side of the vertical noon line are 6 segments of about 15 degrees each, representing morning and afternoon temporal (seasonally uneven) hours. Small dots in the middle of each hourly segment serve for even finer timing. Nevertheless, the hour lines are not drawn with precision.
Read more: 13th Century BCE Ancient Egyptian Sundial Discovered

